Meniscal repair/balancing

Meniscal repair/balancing
What are menisci
There are teo menisci in the knee joint a medial and a lateral,the two menisci of the knee are crescent-shaped wedges that fill the gap between the tibia and femur. The menisci provide joint stability by creating a cup for the femur to sit in. The outer edges are fairly thick while the inner surfaces are thin. If the menisci were missing, the curved femur would have to move on the flat tibia.
The medial meniscus, located on the inside of the knee, is more of an elongated “C”- shape, as the tibial surface is larger on that side. The medial meniscus is more commonly injured because it is firmly attached to the medial collateral ligament and joint capsule. The lateral meniscus, on the outside of the knee, is more circular in shape. The lateral meniscus is more mobile than the medial meniscus as there is no attachment to the lateral collateral ligament or joint capsule.
The meniscus is fibrocartilage that has strength and flexibility from collagen fiber. Its resilience is due to the high water content in the spaces between the cells. There is not much blood supply to the menisci. Blood flows only to the outer edges from small arteries around the joint. The poor blood supply to the inner portion of the meniscus makes it difficult for the meniscus to heal.
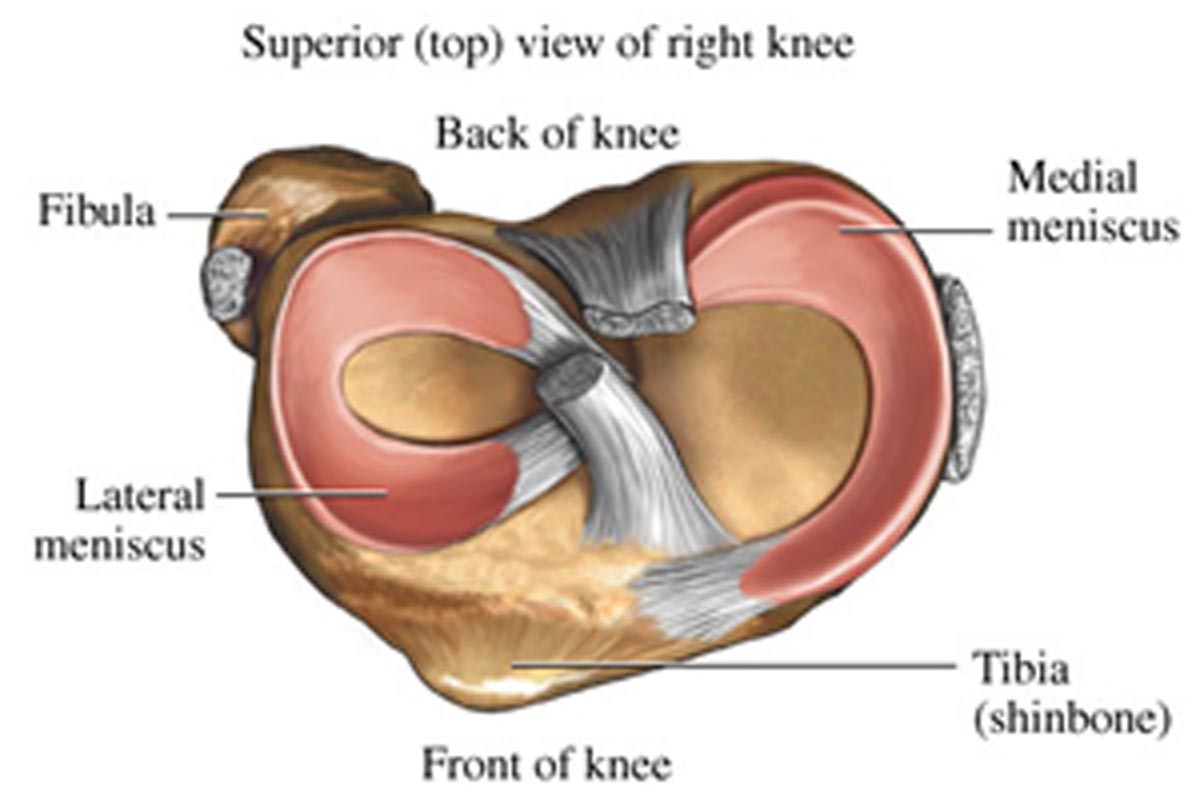
Functions of the menisci
The meniscus acts as a shock absorber for the knee by spreading compression forces from the femur over a wider area on the tibia.The medial meniscus bears up to 50% of the load applied to the medial (inside) compartment of the knee.The lateral meniscus absorbs up to 80% of the load on the lateral (outside) compartment of the knee.During the various phases of the walking cycle, forces shift from one meniscus to the other, and forces on the knee can increase to 2 – 4 times body weight.While running, these forces on the knee increase up to 6 – 8 times body weight. There are even higher forces when landing from a jump.
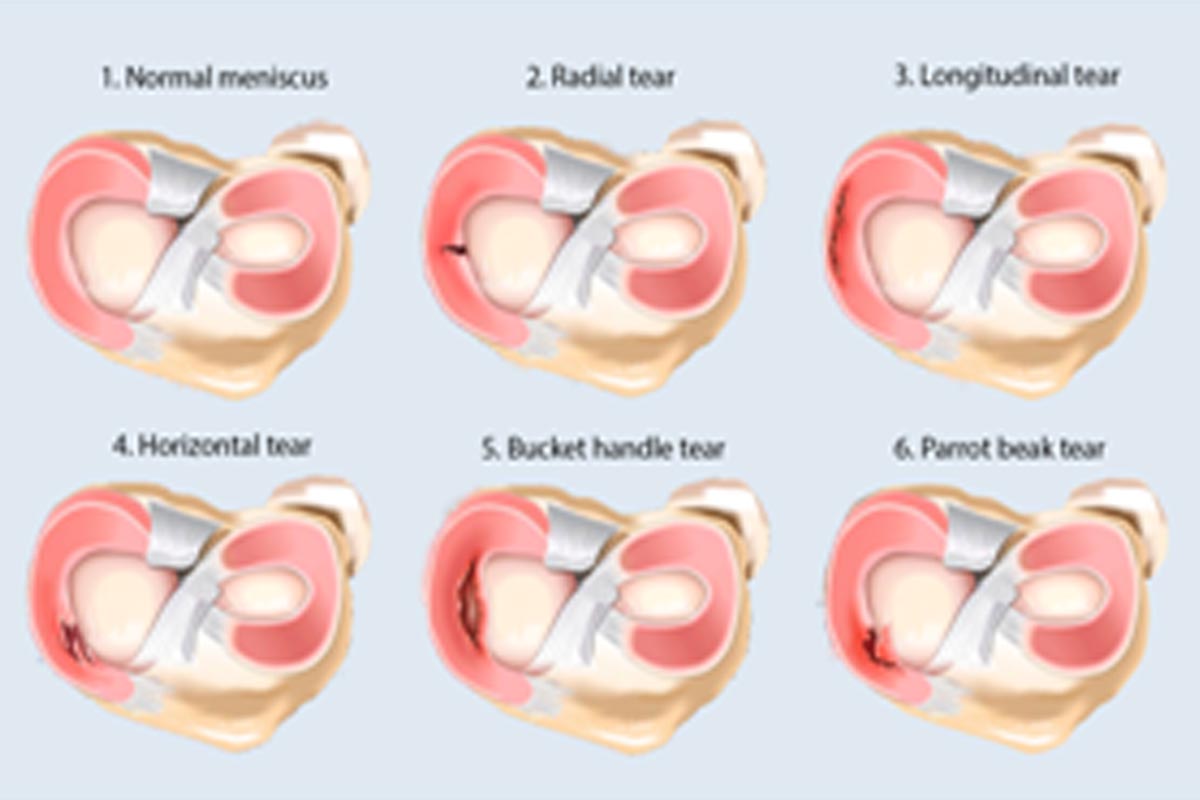
Types of meniscal tear
There are various types of menicalinjurybut the location of the tear generally determines the types of sugery your surgeon might suggests.A tear may be located in the anterior horn, body, or posterior horn. A posterior horn tear is the most common. The meniscus is broken down into the outer, middle, and inner thirds. The third in which the tear is located will determine the ability of the tear to heal, since blood supply in that area is critical to the healing process. Tears in the outer 1/3 have the best chance of healing.
Based on pattern
Types of sugery
Arthroscopic repair
When the tear is located in the outer 1/3rd and is fresh your surgeon will attempt to repair the menisci using special stiches
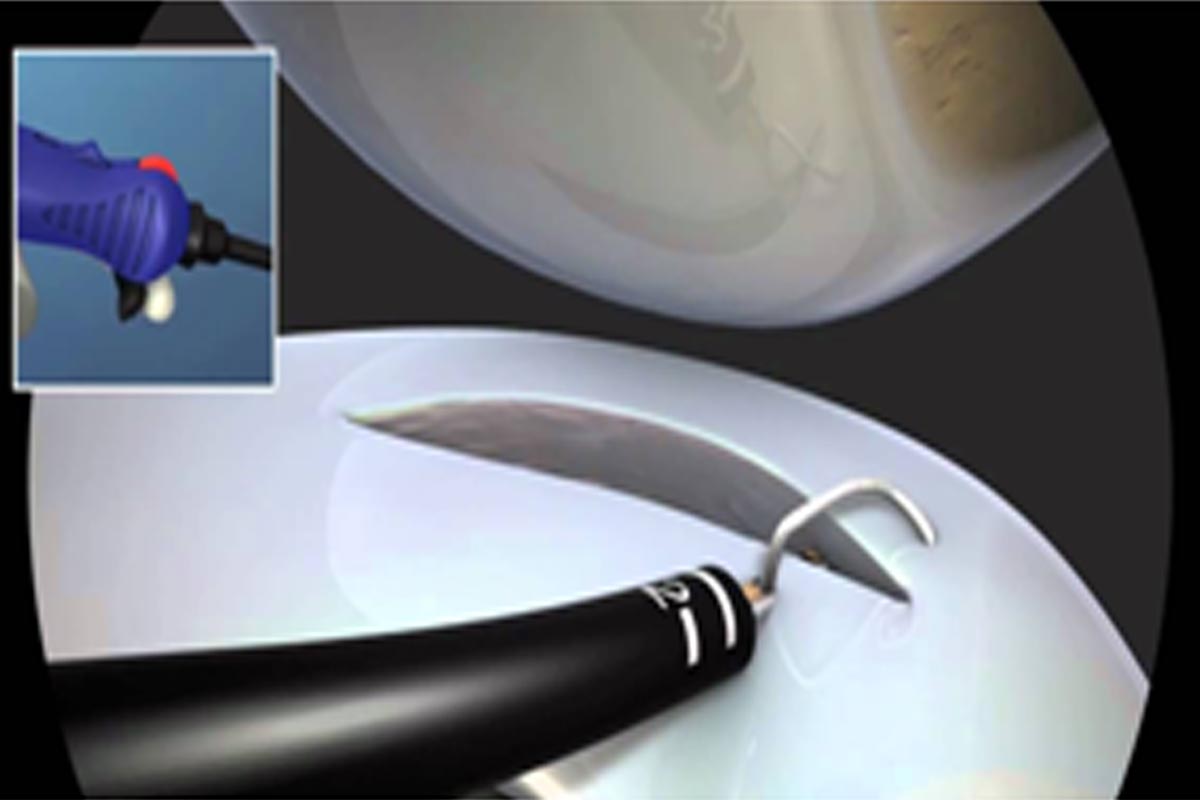
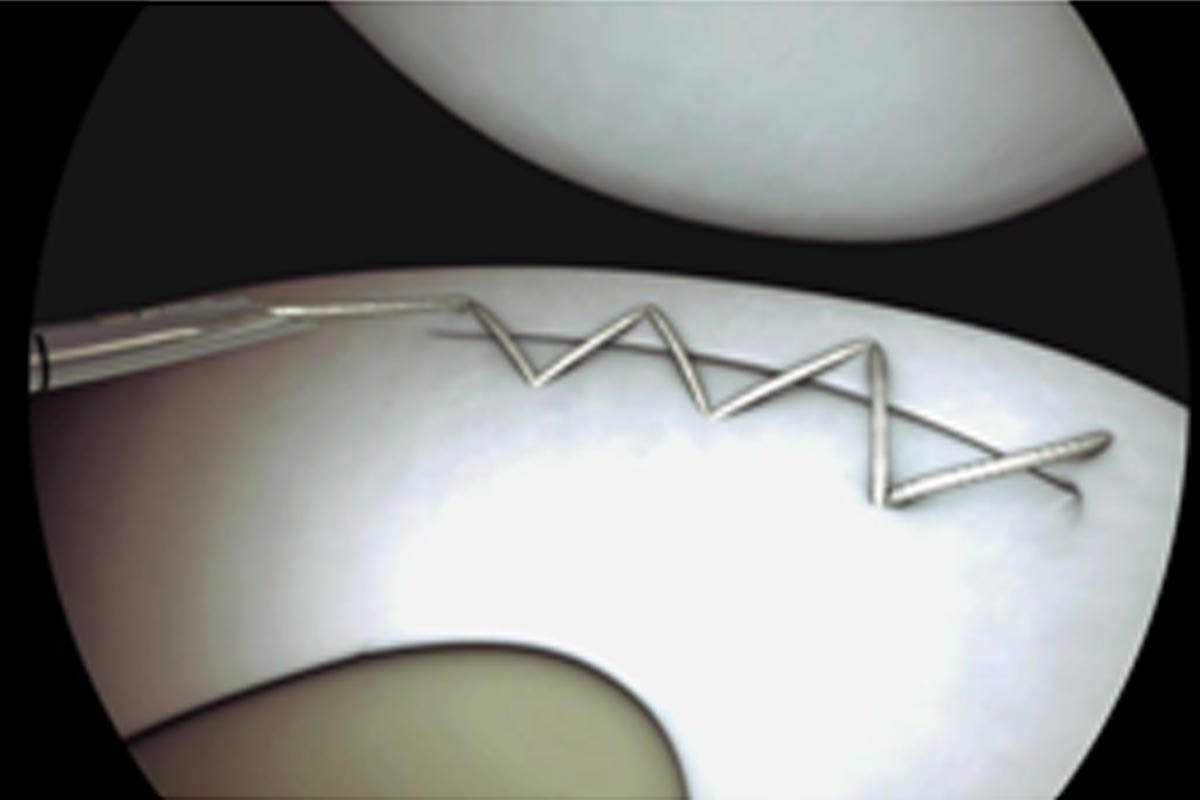
Arthroscopic repair
Incases of chronic meniscal tear or severe complex tears where there is poor blood supply and poor healing your surgeon may suggest removing or partially shaving the affected part of the menisci
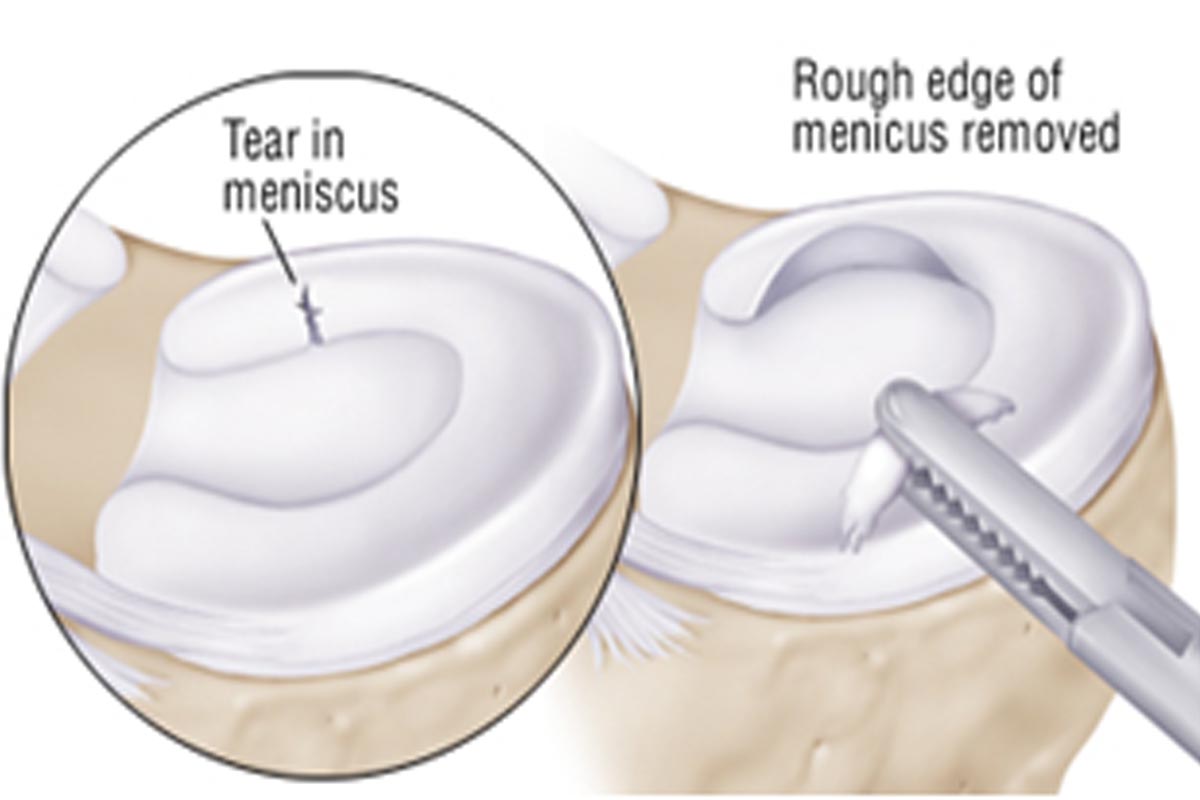
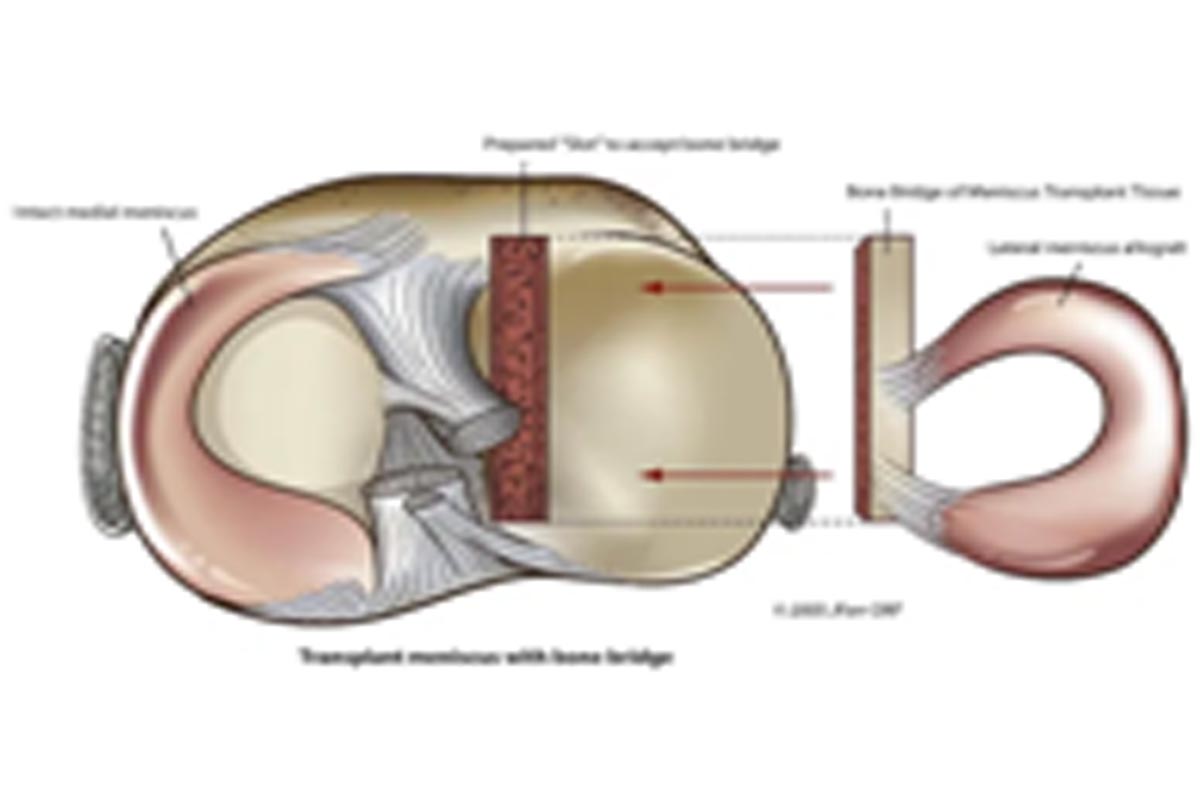
Meniscal Replacement
Experimental attempts to replace damaged meniscus are seen as important recent advances in orthopaedic medicine. The new technology mentioned here has been performed at a few surgical centers across the country on a small number of patients.
Meniscal transplant – This procedure involves transplanting a meniscus from a donor into the injured knee. Only a limited number of surgeons perform this procedure on a routine basis. The long-term outcomes are still being evaluated.